Arthritis means inflammation of the joint. However, arthritis is not a single condition. There are well over 100 kinds of arthritis, all of which affect one or more joints in the body, and some forms of arthritis do not involve any inflammation.
Dr James Fries has developed eight categories of arthritis, which help explain how arthritis affects different structures in the body. Pain, stiffness and inflammation are hallmarks of arthritis with the two common forms being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis, is a progressive degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage associated with risk factors, such as overweight/obesity, history of joint injury and age. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, muscle weakness and cramps or muscle spasm around the infected joint.
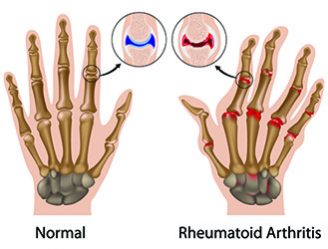
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), a systemic disease characterized by the inflammation of the membranes lining the joint, which causes pain, stiffness, warmth, swelling and sometimes severe joint damage. Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex, frequently progressive disease.
The types of medication used to treat arthritis range from analgesics such as paracetamol and aspirin (also an anti-inflammatory)to prescription medications such as the non-steroidalanti-inflammatory drugs. Physical activity and weight management are important and can help manage the pain and stiffness from many forms of arthritis.
Programming Considerations
- When joints are inflamed, rest is needed but if joints are stiff, they need more activity and movement to relieve the stiffness.
- Altering activities or ensuring adequate rest breaks should be considered when participant suffering from arthritis are involved inactive recreation activities.
- Mobility may be an issue with some people so too much walking is not desirable.
- Swimming in warm water is an excellent activity to relieve the symptoms.
- Bike riding encourages muscle development without straining inflamed joints.
- Arthritis in the hands may affect the ability to grip everyday items and sport and recreation equipment.
- It may be necessary to spend sometime learning how much modification is required for a person with equipment, etc.
Strategies for Inclusion
- Be aware of the limitations and what assistance is needed to participate successfully.
- Avoid activities requiring fine motor skills.
Behaviour Management Issues
- Provide continuous encouragement.
Further information
Arthritis Victoria – www.arthritisvic.org.au